Publications
A Radical Strategy to the Synthesis of Bicyclo[1.1.1]pentyl C−Glycosides
Giulio Goti,* Alessia Marrese, Simone Baldon, Patricia Gómez Roibás, Giorgio Pelosi, Andrea Sartorel and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract
Aryl C-glycosides, in which carbohydrates are directly linked to aryl fragments through a stable C–C bond, are an important class of biologically active molecules widely found in nature. These compounds exhibit resistance to (enzymatic) hydrolysis, a property that has been successfully leveraged in the development of metabolically stable drugs. On the other hand, despite their potential, three-dimensional analogues of aryl C-glycosides remain largely overlooked. Here, we present a three-component radical strategy that grants access to this underexplored chemical space. Here, glycosyl bromides serve as a source of glycosyl radicals, which can react with [1.1.1]propellane and a suitable SOMOphile to afford bicyclopentyl C-glycosides. These C(sp³)-rich analogues replace a planar aryl ring with a three-dimensional bicyclopentyl moiety, which is expected to enhance physicochemical properties. The protocol is practical, mild, and amenable to scalable synthesis in continuous flow. Experimental and computational studies support a radical chain mechanism under kinetic control.
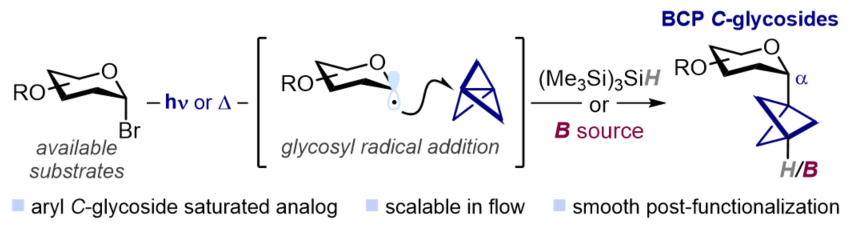
Chem. Sci., 2025, DOI: 10.1039/D5SC07328F.
Triplet state reactivity of iminium ions in organocatalytic asymmetric [2 + 2] photocycloadditions
Vasco Corti, Gianluca Simionato, Lorenzo Rizzo, Stefano A. Serapian, Giorgio Pelosi, Mirco Natali, and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract
Organic transformations mediated by the transient formation of iminium ions have shown remarkable synthetic potential for the construction of chiral molecules. The possibility to access their first singlet excited state (S₁) under light irradiation has led to the development of previously inaccessible transformations. However, the triplet-state (T₁) reactivity remains limited and typically requires external photosensitizers. In this study we show that structurally modified chiral iminium ions, integrated into extended π-systems, directly engage in T₁ reactivity. This modified conjugated architecture was designed to overcome the intrinsic photophysical limitations of conventional iminium ion chemistry, enabling access to previously inaccessible excited-state reaction manifolds. The resulting system allows organocatalytic enantioselective [2 + 2] photocycloadditions without the need for external sensitizers. Mechanistic studies, involving spectroscopic techniques and computational methods elucidates the role of the T₁ intermediate as the key reactive intermediate.
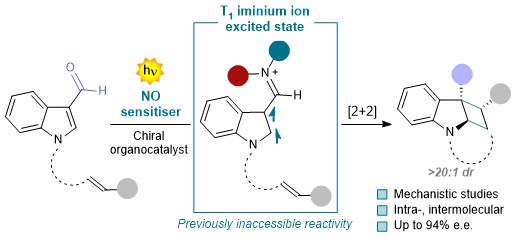
Nat. Chem. 2025, DOI:10.1038/s41557-025-01960-3.
HF-Free Manufacturing of Fluorochemicals from Fluorspar
Ricardo I. Rodríguez, and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract
Fluorochemicals are vital in modern chemistry, from batteries to agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. However, their production still relies on a centuries-old method involving the production of hydrofluoric acid (HF). Recently, Gouverneur and co-workers developed innovative, and more sustainable approaches starting from naturally occurring fluorspar (CaF₂), reducing environmental impact.

Invited highlight on the recent work by Gouverneur and co-workers appeared in Nature, 2024, 635, 359-364. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, e202500255.
Study of tribenzo[b,d,f]azepine as donor in D–A photocatalysts
Katy Medrano-Uribe*, Jorge Humbrías-Martín and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract
Since the discovery of donor–acceptor (D–A) type molecules in the field of materials science, they have found great applicability in the field of photocatalysis. Most of these compounds are based on complex D–A–D structures or multi-D–A systems, such as 4CzIPN. Whereas these systems have been widely studied and applied as photocatalysts, simpler D–A structures remain less explored. Nevertheless, the simplicity of D–A structures makes them the ideal structures to further understand the structure–property relationship of D–A molecules for optimizing their photocatalytic performance by simpler modification of the different D–A subunits. In particular, D–A structures featuring sulfur-based acceptors and nitrogen donors have gained increasing attention for their use as photoredox catalysts. This study introduces a new family of D–A molecules by exploring various sulfur-based acceptors and nitrogen donors, including a novel tribenzo[b,d,f]azepine (TBA) unit and 5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine (IMD). Our findings demonstrate that these simple D–A structures exhibit promising photocatalytic properties, comparable to those of more complex D–A–D systems.
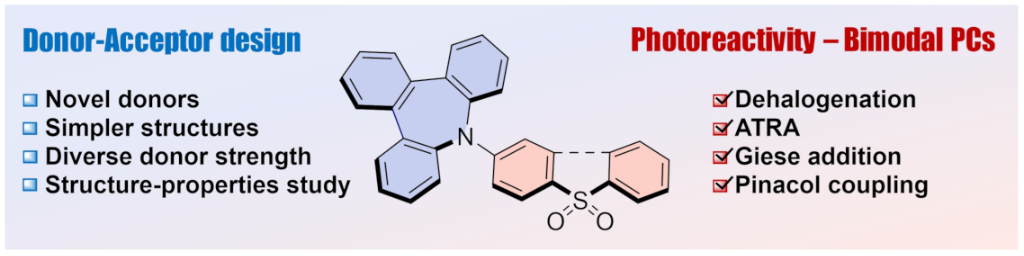
Invited contribution to Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 935–944. DOI:10.3762/bjoc.21.76.
Microfluidic Photocatalytic Ring Expansion of Sulfonium Salts for the Synthesis of Cyclic Sulfides
Jorge Humbrías-Martín, José J. Garrido-González, Katy Medrano-Uribe, Giorgio Pelosi, Loris Laze, and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract Cyclic sulfides are relevant building blocks in medicinal and synthetic chemistry, with applications ranging from drug discovery to materials science. However, the synthesis of medium-sized cyclic sulfides (6-8 membered rings) remains largely underdeveloped. Herein, we report a photocatalytic ring-expansion strategy for sulfonium salts, granting access to six-, seven-, and eight-membered cyclic sulfides with very high regio- and diastereocontrol. The implementation of the method under continuous flow was key to increasing efficiency and minimizing product decomposition. Mechanistic investigations revealed the formation of benzylic radical and carbocation intermediates that control the high regio- and diastereoselectivity observed. Finally, the synthetic utility of this approach was demonstrated in the synthesis of cyclic sulfoxides and sulfones, which are easily obtained from the corresponding sulfide products. .
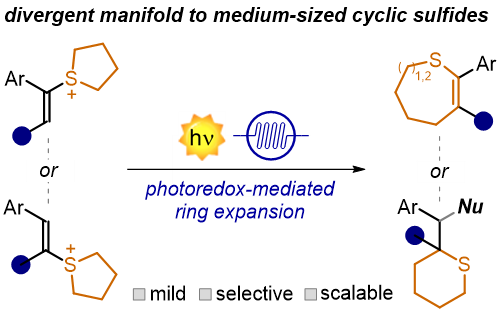
ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 6507−6513. DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.5c01231.
.
Radical photochemical difluorosulfoximination of alkenes and propellanes
Simone Baldon, Julien Paut, Elsa Anselmi, Guillaume Dagousset, Béatrice Tuccio, Giorgio Pelosi, Sara Cuadros*, Emmanuel Magnier*, and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract Herein, we report a metal-free divergent visible-light driven method for the synthesis of fluorinated sulfoximines. Both olefins and propellanes efficiently undergo difluorosulfoximination with yields up to 77% (65 examples). The process is general and robust and tolerates diverse functional groups, including esters, ethers, ketones, silyl groups, silyl ethers or boronic esters. The functionalization of diverse bioactive ingredients (8 examples), as well as various products manipulations demonstrate the synthetic usefulness of the developed synthetic platform. Finally, we rationalized the divergent reaction mechanism performing Stern-Volmer quenching and EPR experiments, that revealed the key activity of a difluoroalkyl sulfoximine radical. .
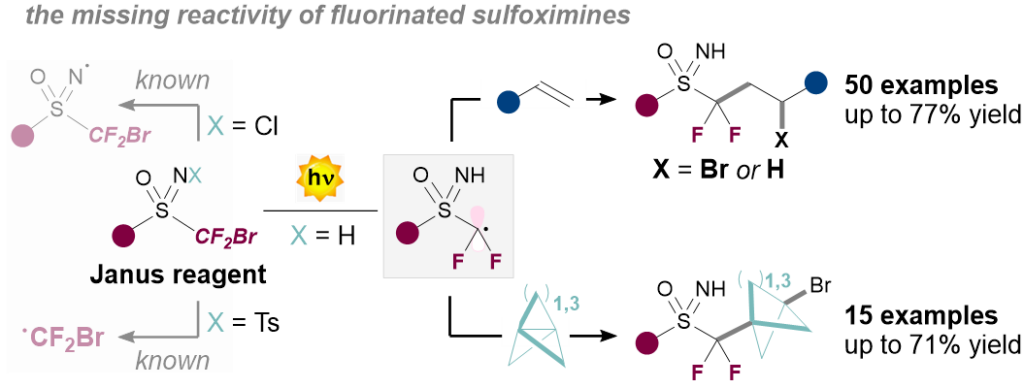
Chem. Sci. 2025, DOI: 10.1039/D5SC01068C.
.
PHOTOCAT24: The Best of the First Edition
Katy Medrano-Uribe, Sara Cuadros, José J. Garrido-González, Giulio Goti, Daniele Mazzarella, and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract With more than 185 attendees, PHOTOCAT24 has been a real success. The photochemical community is vital and vibrant, as the young researchers that have attended the conference. With the help of light, we can perform unique transformations…and we are sure there will be even more to discover and discuss in the future edition. .

Eur. JOC. 2024, e202401316. DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.202401316.
Invited highlight on the First International Conference PHOTOCAT held in Padova in June 2024.
.
Electrochemical Ferrier Rearrangement of Glycals
Chun Qi, Giulio Goti, Andrea Sartorel, Luca Dell’Amico*, and Daniele Mazzarella*
Abstract The Ferrier rearrangement (FR) is a well-documented reaction that relies on strong acids or oxidants to convert glycals into unsaturated glycosyl derivatives. In this work, we introduce an electrochemical variant of the FR, offering a broad substrate compatibility. Various nucleophiles and glycal derivatives afford 2,3-unsaturated glycosyl derivatives in high yields with excellent diastereoselectivities. This sustainable method promises to expand the electrochemistry applications in sugar chemistry. .
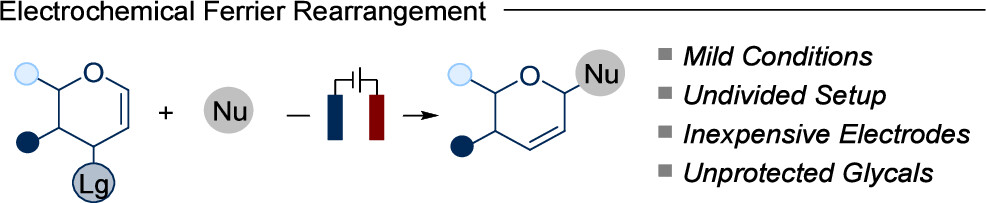
Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 9328–9333. DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.4c03511.
.
Radical strain-release photocatalysis for the synthesis of azetidines
Ricardo I. Rodríguez, Vasco Corti, Lorenzo Rizzo, Stefano Visentini, Marco Bortolus, Agnese Amati, Mirco Natali, Giorgio Pelosi, Paolo Costa, and Luca Dell’Amico *
Abstract The increasing popularity of four-member rings in drug discovery has prompted the synthetic chemistry community to advance and reinvent old strategies to craft these structures. Recently, the strain-release concept has been used to build complex architectures. However, while there are many strategies for accessing small carbocyclic derivatives, the synthesis of azetidines remains underdeveloped. Here, we report a photocatalytic radical strategy for accessing densely functionalised azetidines from azabicyclo[1.1.0]butanes (ABBs). The protocol operates with an organic photosensitiser, which finely controls the key energy-transfer process with distinct types of sulfonyl imines. The radical intermediates are intercepted by the ABB via a radical strain-release process, providing access to difunctionalized azetidines in a single step. This radical process is unfolded by a combination of spectroscopic and optical techniques and density functional theory calculations. The power and generality of this method is illustrated with the synthesis of various azetidine targets, including derivatives of celecoxib and naproxen. .
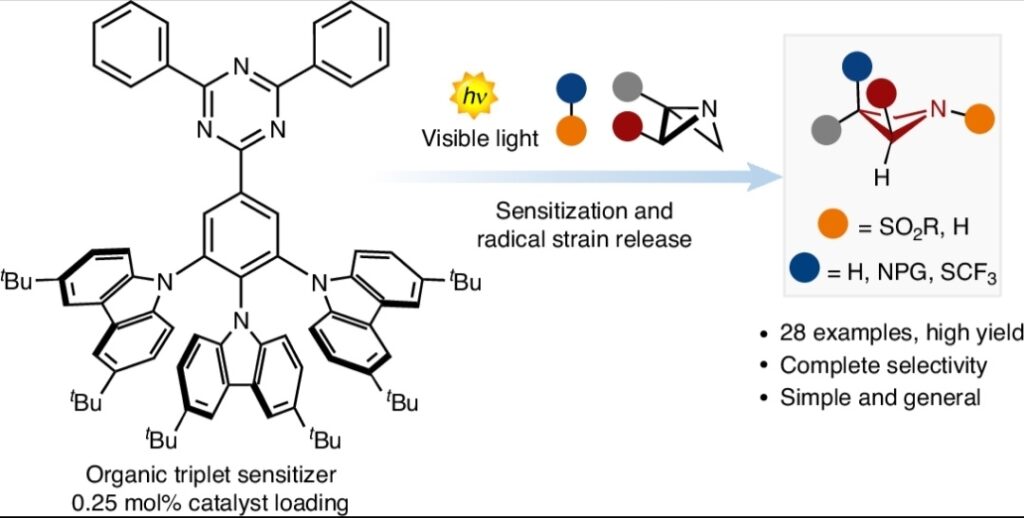
Nature Catal. 2024, DOI: 10.1038/s41929-024-01206-4.
For a preprint version see: https://chemrxiv.org.
Highlighted in News & Views – Nat. Catal. 2024, DOI: 10.1038/s41929-024-01254-w
Highlighted in Synfacts 2024; 20, 1195, DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1775130
.
Photocatalytic a-Difluoroalkoxyketones Synthesis via Radical Intermolecular Alkoxylation of Difluoroenol Silyl Ethers
Julien Paut, Simone Baldon, Elsa Anselmi, Luca Dell’Amico,* Guillaume Dagousset,* and Emmanuel Magnier*
Abstract Here, we present a new metal-free organophotoredox-catalysed approach for the synthesis of difluoroalkoxylated ketones. This approach involves alkoxyl radicals generated from pyridinium salts by the activity of a purely organic photocatalyst. This mild process tolerates several functional groups and can be scaled up to gram scale. Diverse products manipulations accounts for the versatility of the obtained fluorinated products, highlighting the synthetic usefulness of this method. .
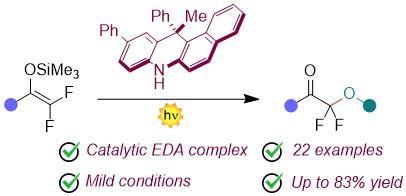
Invited contribution to the issue Fluorine Chemistry: An Outlook to the Future – Adv. Synth. Catal. 2024, 366, 3500 – 3504. DOI: 10.1002/adsc.202400510.
.
Functionalization of Sulfones, Sulfonamides and Sulfoximines
José J. Garrido-González, Katy Medrano-Uribe, Cristian Rosso, Jorge Humbrías-Martín, and Luca Dell’Amico *
Abstract Sulfur(VI)-based functional groups are popular scaffolds in a wide variety of research fields including synthetic and medicinal chemistry, as well as chemical biology. The growing interest in sulfur(VI)-containing molecules has motivated the scientific community to explore new methods to synthesize and modify them. Here, photocatalysis plays a key role granting access to new types of reactivity under mild reaction conditions. In this Perspective, we present a selection of works reported in the last six years focused on the photocatalytic assembly and reactivity of sulfones, sulfonamides, and sulfoximines. We addressed the key synthetic intermediates for each transformation, while discussing limitations and strength points of the protocols. Future directions of the field are finally presented. .
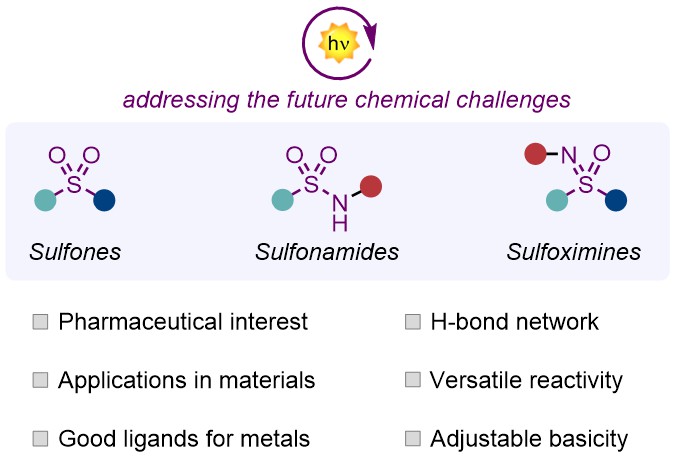
Invited perspective article – Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202401307.
.
Electrochemical Asymmetric Radical Functionalization of Aldehydes Enabled by a Redox Shuttle
Daniele Mazzarella,* Chun Qi, Michael Vanzella, Andrea Sartorel, Giorgio Pelosi, and Luca Dell’Amico *
Abstract Aminocatalysis is a well-established tool that enables the production of enantioenriched compounds under mild conditions. Its versatility is underscored by its seamless integration with various synthetic approaches. While the combination of aminocatalysis with metal catalysis, photochemistry, and stoichiometric oxidants has been extensively explored, its synergy with electrochemical activation remains largely unexplored. Herein, we present the successful merger of electrochemistry and aminocatalysis to perform SOMO-type transformations, expanding the toolkit for asymmetric electrochemical synthesis. The methodology harnesses electricity to drive the oxidation of catalytically generated enamines, which ultimately partake in enantioselective radical processes, leading to α-alkylated aldehydes. Crucially, mechanistic studies highlight how this electrochemical strategy is enabled by the use of a redox shuttle, 4,4’-dimethoxybiphenyl, to prevent catalyst degradation and furnishing the coveted compounds in good yield and high enantioselectivity.. .
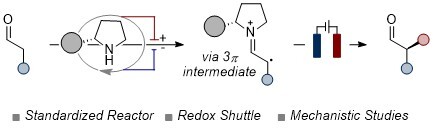
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2024. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202401361.
.
The impact of UV-light on synthetic photochemistry and photocatalysis
Giulio Goti, Kavyasree Manal, Jayaraman Sivaguru,* and Luca Dell’Amico *
Abstract During the past 15 years, an increasing number of research groups have embraced visible-light-mediated synthetic transformations as a powerful strategy for the construction and functionalization of organic molecules. This trend has followed the advent and development of photocatalysis, which often operates under mild visible-light irradiation. Nowadays, the general perception of UV-light photochemistry is often as an out-of-fashion approach that is difficult to perform and leads to unselective reaction pathways. Here we wish to propose an alternative and more realistic point of view to the scientific community. First, we will provide an overview of the use of UV light in modern photochemistry, highlighting the pivotal role it still plays in the development of new, efficient synthetic methods. We will then show how the high levels of mechanistic understanding reached for UV-light-driven processes have been key in the implementation of the related visible-light-driven transformations. .
Nat. Chem., 2024. DOI: s41557-024-01472-67333.
.
Light-Driven Synthesis and Functionalization of Bicycloalkanes, Cubanes and Related Bioisosteres
Sara Cuadros, Julien Paut, Elsa Anselmi, Guillaume Dagousset, Emmanuel Magnier, and Luca Dell’Amico *
Abstract This Review aims to provide an overview on the recent photochemical strategies for the construction and/or functionalization of bicycloalkanes, cubanes, and some of their heterocyclic structural analogues. The synthetic methods have been organized according to the molecular target, and with a particular emphasis on the type of photochemical mechanisms involved. Future perspectives and open synthetic challenges within the field are presented. .
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2024, e202317333. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202317333.
.
Photocatalytic (3+2) Dipolar Cycloadditions of Aziridines Driven by Visible-Light
Daniele Mazzarella, Tommaso Bortolato, Giorgio Pelosi and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract Herein, we document the design and development of a novel (3+2) cycloaddition reaction aided by the activity of an organic photocatalyst and visible light. The process is extremely fast, taking place in a few minutes, with virtually complete atom economy. A large variety of structurally diverse aziridines were used as masked ylides in presence of different types of dipolarophiles (28 examples with up to 94% yield and >95:5 dr). Mechanistic insights, encompassing both photophysical, electrochemical and experimental methods highlight that the chemistry is driven by the in-situ generation of the reactive ylide trough two consecutive electron-trasfer processes. We also report an aerobic cascade process, where an additional oxidation step grants access to a vast arrays of pyrrole derivatives (19 examples with up to 95% yield). Interestingly, the extended aromatic core exhibits a distinctive absorption and emission profile, that can be easily used to tag the effectiveness of this covalent linkage.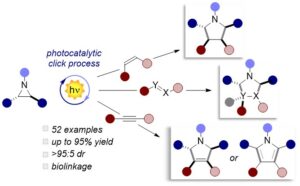
Chem. Sci. 2023, DOI: 10.1039/D3SC05997A.
.
A General Organophotoredox Strategy to Difluoroalkyl Bicycloalkane (CF2-BCA) Hybrid Bioisosteres
Sara Cuadros, Giulio Goti, Giorgia Barison, Alfredo Raulli, Tommaso Bortolato, Giorgio Pelosi, Paolo Costa and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract Here, we report a general approach to the synthesis of the difluoroalkyl bicycloalcanes (CF2-BCAs), as structural surrogates of aryl ketones and ethers. The chemistry is driven by a dihydrobenzoacridine photocatalyst, that engages in a catalytic electron-donor acceptor (EDA) complex, or directly reduces the fluorinated substrate. These two convergent manifolds lead to the generation of the R-CF2 radical, that reacts with the [1.1.1]- or [3.1.1.]-propellane. The method is extremely general, and extendable to complex bioactive molecules (30 examples, up to 87% yield). The structural features of the CF2-BCP hybrid bioisostere were investigated by single crystal X-ray. Finally, we synthesised a CF2-BCP analogue of a Leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitor, replacing the original aryl ether motif. In-silico docking studies indicated that this new analogue maintains the same arrangement within the enzyme pocket, profiling the use of the CF2-BCA hybrid bioisostere in medicinal chemistry settings.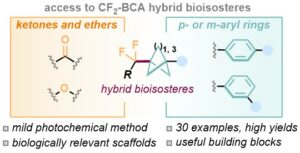 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, DOI: 10.1002/ange.20230358 5.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, DOI: 10.1002/ange.20230358 5.
Among the most read papers in June 2023
.
Self-assembly of benzophenone-diphenylalanine conjugate into a nanostructured photocatalyst
Simone Adorinni, Giulio Goti, Lorenzo Rizzo, Federica Grassi, Slavko Kralj, Fatima Matroodi, Mirco Natali, Rita De Zorzi, Silvia Marchesan,* and Luca Dell’Amico*
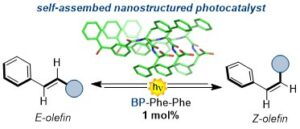
Abstract The conjugation of photoactive benzophenone with diphenylalanine yielded a self-assembling photocatalyst that was probed in the E→Z photoisomerisation of stilbene derivatives.
Invited contribution to the Chem. Commun. themed collection: 2023 Pioneering Investigators – Chem. Commun. 2023, DOI: 10.1039/D3CC01673K.
.
Building C–C bridges with oxalic acid as a traceless keystone
Daniele Mazzarella, and Luca Dell’Amico*
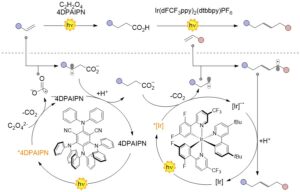
Abstract The construction of C–C bonds from underused feedstock is one of the “holy grails” in organic synthesis. In this issue of Chem, Wu, Lu, and co-workers report a method that makes use of photocatalysis and oxalic acid to promote the reductive cross-coupling of alkenes in a two-step procedure.
Invited preview article – Chem 2023, 4, 766–768. DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2023.03.024.
For the original work by Wu, Lu and co-workers see Chem, 2022, 4, 978-988. DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2022.12.013.
.
A Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer Strategy to the Redox-Neutral Photocatalytic CO2 Fixation
Pietro Franceschi, Elena Rossin, Giulio Goti, Angelo Scopano, Alberto Vega-Peñaloza, Mirco Natali, Deepak Singh, Andrea Sartorel,* and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract Herein, we report our study on the design and development of a novel photocarboxylation method with CO2. We have used an organic photoredox catalyst (PC, 4CzIPN) and differently substituted dihydropyridines (DHPs) in combination with an organic base (1,5,7-triazabicyclodec-5-ene, TBD) to access a proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) based manifold. In depth mechanistic investigations performed merging experimental analysis (NMR, IR, cyclic voltammetry) and density-functional theory (DFT) calculations reveal the key activity of a H-bonding complex between the DHP and the base. The thermodynamic and kinetic benefits of the PCET mechanism allowed the implementation of a redox-neutral fixation process leading to synthetically relevant carboxylic acids (18 examples with isolated yields up to 75%) under very mild reaction conditions. Finally, diverse product manipulations were performed to demonstrate the synthetic versatility of the obtained products.
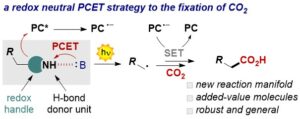
J. Org. Chem. 2023, DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c02952.
Invited contribution to the JOC Special Issue “Progress in Photocatalysis for Organic Chemistry”.
Among the most read papers in February 2023
.
Mechanisms and Synthetic Strategies in Visible-Light-Driven [2+2]-Heterocycloadditions
Pietro Franceschi, Sara Cuadros, Giulio Goti, and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract The synthesis of four membered heterocycles usually requires multi-step procedures and prefunctionalized reactants. A straightforward alternative is the photochemical [2+2]-heterocycloaddition between an alkene and a carbonyl derivative, conventionally based on the photoexcitation of this latter. However, this approach is limited by the absorption profile of the carbonyl, requiring in most of the cases the use of high-energy UV-light, that often results in undesired side reactions and/or the degradation of the reaction components. The development of new and milder visible light-driven [2+2]-heterocycloadditions is, therefore, highly desirable. In this Review, we highlight the most relevant achievements in the development of [2+2]-heterocycloadditions promoted by visible light, with a particular emphasis on the involved reaction mechanisms. The open challenges will also be discussed, suggesting new possible evolution, and stimulating new methodological developments in the field. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, DOI: 10.1002/anie.202217210
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, DOI: 10.1002/anie.202217210
Among the most read papers in January 2023
.
The Rational Design of Reducing Organophotoredox Catalysts Unlocks Proton-Coupled Electron-Transfer and Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization Mechanisms
Tommaso Bortolato, Gianluca Simionato, Marie Vayer, Cristian Rosso, Lorenzo Paoloni, Edmondo M. Benetti, Andrea Sartorel, David Lebœuf,* and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract Photocatalysis has become a prominent tool in the arsenal of organic chemists to develop and (re)imagine transformations, but only a handful of versatile organic photocatalysts (PCs) are available, hampering the discovery of new reactivities. Here, we report the design and complete physicochemical characterization of 9-aryl dihydroacridines (9ADA) and 12-aryl dihydrobenzoacridines (12ADBA) as strong reducing organic PCs. Punctual structural variations modulate their molecular orbital distributions and unlock locally or charge-transfer (CT) excited states. The PCs presenting a locally excited state showed better performances in photoredox defunctionalization processes (yields up to 92%), whereas the PCs featuring a CT excited state produced promising results in atom transfer radical polymerization under visible light (up to 1.21 Đ, and 98% I*). Unlike all the PCs classes reported so far, 9ADA and 9ADBA feature a free NH group, that enables a catalytic multi-site proton-coupled electron transfer (MS-PCET) mechanism. This manifold allows the reduction of redox-inert substrates including aryl, alkyl halides, azides, phosphate and ammonium salts (Ered up to – 2.83 vs. SCE) under single-photon excitation. We anticipate that these new PCs will open new mechanistic manifolds in the field of photocatalysis by allowing access to previously inaccessible radical intermediates under one-photon excitation.
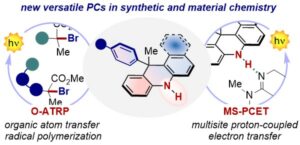
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, DOI:10.1021/jacs.2c11364
Among the most read papers in January 2023
.
Unveiling the impact of the light source and steric factors on [2 + 2] heterocycloaddition reactions
Javier Mateos, Francesco Rigodanza, Paolo Costa, Mirco Natali, Alberto Vega-Peñaloza, Elisa Fresch, Elisabetta Collini, Marcella Bonchio, Andrea Sartorel, and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract Information gained from in-depth mechanistic investigations can be used to control the selectivity of reactions, leading to expansion of the generality of synthetic processes and discovery of new reactivity. Here, we investigate the mechanism of light-driven [2 + 2] heterocycloadditions (Paternò–Büchi reactions) between indoles and ketones to develop insight into these processes. Using ground-state ultraviolet–visible absorption and transient absorption spectroscopy, together with density functional theory calculations, we found that the reactions can proceed via an exciplex or electron–donor–acceptor complex, which are key intermediates in determining the stereoselectivity of the reactions. We used this discovery to control the diastereoselectivity of the reactions, gaining access to previously inaccessible diastereoisomeric variants. When moving from 370 to 456 nm irradiation, the electron–donor–acceptor complex is increasingly favoured, and the diastereomeric ratio (d.r.) of the product moves from >99:<1 to 47:53. In contrast, switching from methyl to ipropyl substitution favours the exciplex intermediate, reversing the d.r. from 89:11 to 16:84. Our study shows how light and steric parameters can be rationally used to control the diastereoselectivity of photoreactions, creating mechanistic pathways to previously inaccessible stereochemical variants.
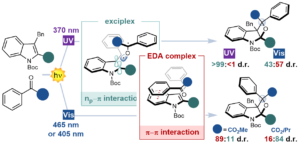
Nat. Synth. 2022. DOI: 10.1038/s44160-022-00191-5.
For a preprint version see: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1676011/v1
Highlighted in News & Views – Nat. Synth., 2022, DOI: 10.1038/s44160-022-00200-7
.
Giving ketones the green light
Giulio Goti, and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract The α-arylation of ketones is a powerful synthetic strategy for the construction of C–C bonds, but general metal-free methods are scarce. Now, a green-light-mediated photoredox protocol enables this transformation, giving access to a broad range of useful building blocks and value-added biorelevant products.
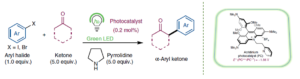
News & Views invited article – Nat. Synth. 2022, 1, 101–102. DOI: 10.1038/s44160-022-00026-3
For the original work by Gianetti and co-workers see Nat. Synth., 2022, 1, 147-157. DOI: s44160-021-00021-0.
.
The Photochemical Activity of a Halogen-Bonded Complex Enables the Microfluidic Light-Driven Alkylation of Phenols
Sara Cuadros, Cristian Rosso, Giorgia Barison, Paolo Costa, Marcella Bonchio, Maurizio Prato, Giacomo Filippini,* and
Abstract A mild light-driven protocol for the direct alkylation of phenols is reported. The process is driven by the photochemical activity of a halogen-bonded complex formed upon complexation of the in situ generated electron-rich phenolate anion with the α-iodosulfone. The reaction proceeds rapidly (10 min) under microfluidic conditions, delivering a wide variety of ortho-alkylated products (27 examples, up to 97% yield, >20:1 regioselectivity, on a gram scale), including densely functionalized bioactive phenol derivatives.
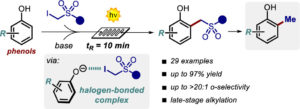
Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 2961–2966. DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c00604 – Open access as author choice.
Among the most read papers in May 2022
.
Unveiling the Synthetic Potential of Substituted Phenols as Fully Recyclable Organophotoredox Catalysts for the Iodosulfonylation of Olefins
Cristian Rosso, Sara Cuadros, Giorgia Barison, Paolo Costa, Marcella Bonchio, Maurizio Prato, Luca Dell’Amico,* Giacomo Filippini*
Abstract We describe an efficient photocatalytic procedure for the direct iodosulfonylation of terminal olefins 3 with α-iodo phenylsulfones 4. Specifically, the process uses the simple, robust, and fully recyclable phenol derivative 6e as the precatalytic system and occurs with visible-light irradiation (450 nm). Mechanistic investigations proved the key role of the in situ generated photocatalyst, namely phenolate anion 7e, which has shown high catalytic activity and considerable stability toward the operating conditions. Importantly, this photocatalytic transformation provides a wide variety of densely functionalized alkyl iodides 5 (23 examples, up to 95% yield). Finally, the synthetic potential of this photochemical transformation was demonstrated by scaling up the process under microfluidic conditions (up to 0.67 mmol h–1) while accessing a series of relevant product manipulations.
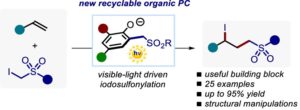
ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 4290−4295. DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.2c00565 – Open access as author choice.
Highlighted by Prof. Douglass F. Taber @organic_portal
https://www.organic-chemistry.org/Highlights/2023/23January.shtm
.
Properties and Synthetic Performances of Phenylamino Cyanoarenes under One-Photon Excitation Manifolds
Tommaso Bortolato, Mateusz Dyguda, Alberto Vega-Penaloza,* and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract The synthesis of a set of new organic photocatalysts (PCs) with a donor-acceptor carbazolyl dicyanobenzene structure is reported. The PCs developed have fine-tailored redox potentials from -1.62 V (PC•+/PC*) to 1.36 V (PC*/PC•-) and have been accessed through a straightforward two-step synthesis. The potential of these PCs was demonstrated in synthetically relevant photoreactions with mechanistic opposite thermodynamic requirements, previously reported only in the presence of precious Ir-based PCs. Interestingly, the herein reported purely organic PCs outperformed the well-established 4CzIPN organic dye under both types of reaction manifolds.
Synthesis 2022, DOI: 10.1055/a-1776-0929. Invited contribution to the Bürgenstock Conference 2021 issue of Synthesis.
.
The Advent and Development of Organophotoredox Catalysis
Tommaso Bortolato, Sara Cuadros, Gianluca Simionato, and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract In the last decade, photoredox catalysis has unlocked unprecedented reactivities in synthetic organic chemistry. Seminal advancements in the field have involved the use of well-studied metal complexes as photoredox catalysts (PCs). More recently, the synthetic community, looking for more sustainable approaches, is moving towards the use of purely organic molecules. Organic PCs are generally cheaper and less toxic, while allowing their rational modification to an increased generality. Furthermore, organic PCs have allowed reactivities that are inaccessible by using the common metal complexes. Likewise in synthetic catalysis, the field of photocatalysis is now experiencing a green evolution moving from metal-catalysis to organocatalysis. In this Feature Article we discuss and critically comment the scientific reasons of this ongoing evolution in the field of photoredox catalysis, showing how and when organic PCs can efficiently replace their metal counterparts.
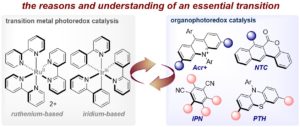
Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 1263–1283. DOI: 10.1039/D1CC05850A
.
Radical α-Trifluoromethoxylation of Ketones under Batch and Flow Conditions by Means of Organic Photoredox Catalysis
Thibaut Duhail, Tommaso Bortolato, Javier Mateos, Elsa Anselmi, Benson Jelier, Antonio Togni, Emmanuel Magnier,* Guillaume Dagousset,* and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract The first light-driven method for the α-trifluoromethoxylation of ketones is reported. Enol carbonates react with the N-trifluoromethoxy-4-cyano-pyridinium, using the photoredox-catalyst 4-CzIPN under 456 nm irradiation, affording the α-trifluoromethoxy ketones in up to 50% isolated yield and complete chemoselectivity. As shown by 29 examples, the reaction is general and proceeds very rapidly under batch (1h) and flow conditions (2min). Diverse product manipulations demonstrate the synthetic potential of the disclosed method to accessing elusive trifluoromethoxylated bioactive ingredients.
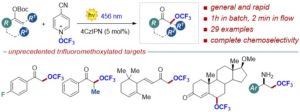
Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 7088–7093. DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c02494 – Open access as author choice
Highlighted in Synfacts 2021, 17, 1294, DOI: 10.1055/s-0041-1737064
Among the most read papers in September 2021
.
Unlocking the Synthetic Potential of Light-Excited Aryl ketones – Applications in Direct Photochemistry and Photoredox Catalysis
Javier Mateos, Sara Cuadros, Alberto Vega-Peñaloza, and Luca Dell’Amico *
Abstract In this account article, we summarize the contributions of our group to the field of photochemistry and photocatalysis. Our work deals with the development of novel synthetic methods based on the exploitation of photoexcited aryl ketones. The application of new technologies, such as microfluidic photoreactors (MFPs), have enhanced the synthetic performance and scalability of several photochemical methods i.e. Paternò–Büchi and photoenolization/Diels-Alder processes, while opening the way to unprecedented reactivity. Further, the careful mechanistic analysis of the developed methods has been instrumental to disclosing a new family of powerful organic photocatalyst able to mediate several thermodynamically extreme photoredox processes.
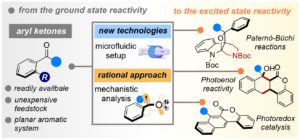
Synlett . 2022, DOI: 10.1055/a-1403-4613 – Contribution to the EuCheMS Organic Division Young Investigator Workshop of Synlett
.
A Rational Approach to Organo‐Photocatalysis. Novel Designs and Structure‐Property‐Relationships
Alberto Vega-Peñaloza, Javier Mateos, Xavier Companyó, Margarita Escudero-Casao, and Luca Dell’Amico *
Abstract Organic photocatalysts (PCs) are emerging as viable and more sustainable tools with respect to metal complexes. Recently, the field of organo‐photocatalysis has experienced an explosion in terms of applications, redesign of well‐established systems and identification of novel scaffolds. A rational approach to the structural modification of the different PCs is key to accessing unprecedented reactivity, while improving their catalytic performances. We herein discuss the concepts underpinning the scaffold modifications of some of the most recently used PCs, analysing how specific structural changes alter their physicochemical and redox properties.

Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 133, 1096-1111. DOI: 10.1002/ange.202006416
Among the most cited papers in 2022
.
Microfluidic Visible-Light Paternò-Büchi Reaction of Oxindole Enol Ethers
Pietro Franceschi, Javier Mateos, Alberto Vega-Peñaloza,* and Luca Dell’Amico *
Abstract A novel microfluidic visible-light process for the functionalisation of oxindoles is reported. The chemistry is based on the reactivity of the corresponding enol ethers, which participate in a site-, regio- and diastereoselective [2+2] heterocycloaddition (Paternò–Büchi) process. The mild reaction conditions, the use of available ketones, together with the high generality (23 examples) and robustness (up to gram scale) make of this process a useful synthetic platform for the construction of structurally strained heterocycles.
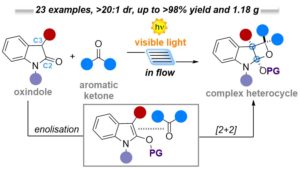
Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2020, 6718-6722. DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.202001057 – Invited contribution to the YourJOC Talents collection 2020
Highlighted in ChemistryView: Microfluidic, Light-Driven Process for Oxindole Functionalization
.
Visible-Light Paternò-Büchi Dearomatisation Process Towards the Construction of Oxeto-Indolinic Polycycles
Javier Mateos, Alberto Vega-Peñaloza, Pietro Franceschi, Francesco Rigodanza, Xavier Companyó,* Philip Andreetta, Giorgio Pelosi, Marcella Bonchio, and Luca Dell’Amico *
Abstract A variety of highly functionalised N-containing polycycles (35 examples) are synthetised from simple indoles and aromatic ketones through a mild visible-light Paternò-Büchi process. Tetrahydrooxeto[2,3-b]indole scaffolds, with up to three contiguous all-substituted stereocenters, are generated in high yield (up to >98%) and excellent site- regio- and diastereocontrol (>20:1). The use of visible light (405 or 465 nm) ensures enhanced performances by switching off undesired photodimerisation side reactions. The reaction can be easely implemented under a microfluidic photoreactor with improved productivity (up to up to 0.176 mmol·h-1) and generality. Mechanistic investigations revealed that two alternative reaction mechanisms can account for the excellent regio- and diasterecontrol observed.
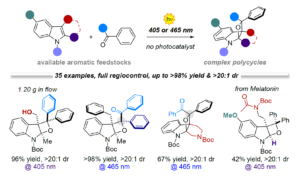
Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 6532-6538. DOI: 10.1039/D0SC01569E
h
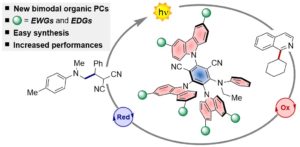
Naphthochromenones: Organic Bimodal Photocatalysts Engaging in Both Oxidative and Reductive Quenching Processes
Javier Mateos, Francesco Rigodanza, Alberto Vega, Andrea Sartorel, Mirco Natali, Tommaso Bortolato, Giorgio Pelosi, Xavier Companyó, Marcella Bonchio, Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract 12 different naphthochromenone photocatalysts (PCs) have been synthesized at gram–scale, combining absorption features across the UV–Vis spectrum, up to 440 nm with an extremely wide redox window (up to 3.22 eV) that is accessible using simple visible light irradiation sources (CFL or LED). Their excited state redox potentials, PC*/PC ●– = up to 1.65 V and PC ●+ /PC* up to –1.77 V vs SCE, are such that these novel PCs can engage in both oxidative and reductive quenching mechanisms with strong thermodynamic requirements . Converging absorption/emission spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry we delineate robust structure–properties relationships, that are further supported by time–dependent density functional theory (TD–DFT) calculations. The potential of these bimodal PCs has been benchmarked in thermodynamically challenging photocatalytic processes, were strong oxidative (> 1.46 V) and strong reductive power (< –1.96 V) is required. Further advantages are given by their simple recovery and reuse – up to four times, without any significant loss in their photocatalytic performances. The ability of efficiently catalysing mechanistically opposite oxidative/reductive photoreactions is a unique feature for organic photocatalysts. This new class of molecules represents a decisive advancement towards generality, sustainability and cost efficiency in photoredox catalysis.
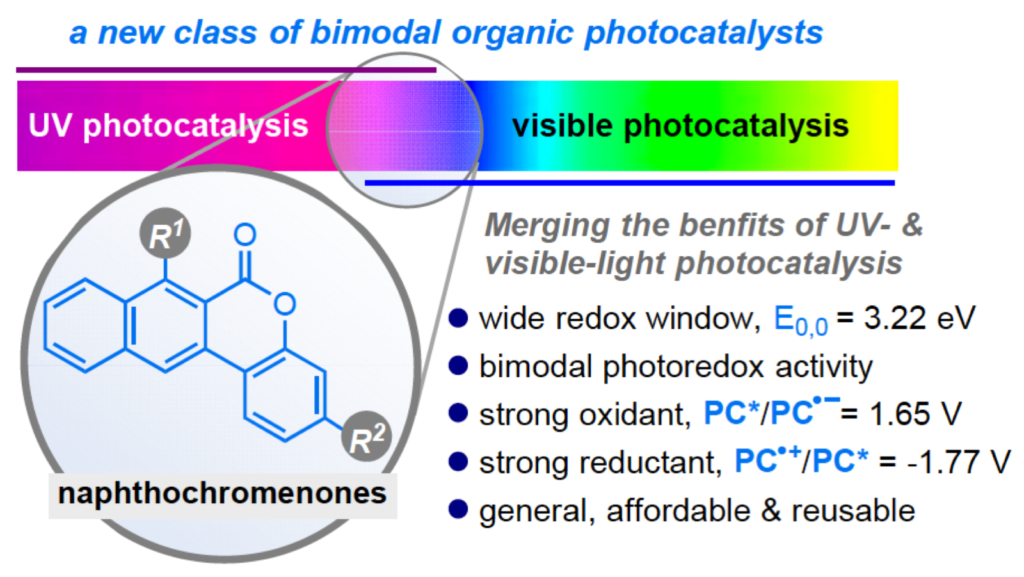
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1302-1312. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201912455
Profiling the Privileges of Pyrrolidine-Based Catalysts in Asymmetric Synthesis: From Polar to Light-Driven Radical Chemistry
Alberto Vega-Peñaloza, Suva Paria, Marcella Bonchio, Luca Dell’Amico*, Xavier Companyó*
Abstract Asymmetric catalysis is a rapidly evolving field in synthetic chemistry. This is due to the growing needs of stereoselective synthetic routes to access enantiopure natural products and bioactive molecules. An efficient approach involves the use of readily available and robust catalysts, while ensuring high yields and stereocontrol. In this scenario, the pyrrolidine-based catalyst has played a dominant role over the past decades. Interestingly, simple scaffold modifications result in dramatic physicochemical and reactivity changes. These features have facilitated the generation of different catalyst variants for the development of highly diversified asymmetric transformations. In this Perspective, we analyze the structural evolution of the pyrrolidine-based catalyst, moving from polar to light-induced radical processes. We discuss the concepts underpinning the most relevant scaffold modifications while defining structure–reactivity relationships. The present work will encourage a rational scaffold design toward unprecedented reactivity pathways and improved catalytic performances.
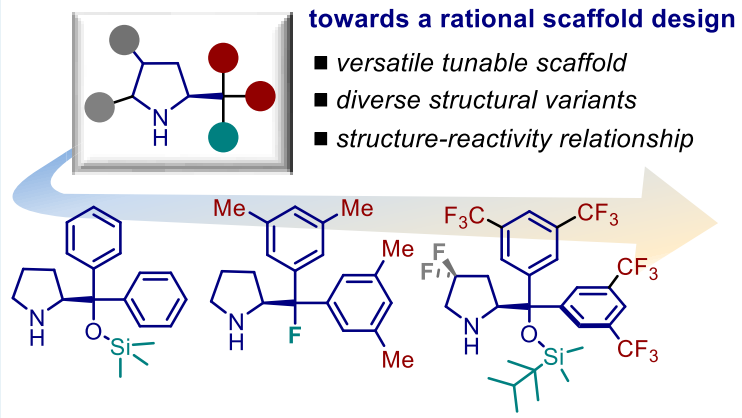
ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 6058-6072. DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.9b01556
Acetaldehyde Silyl Enol Ethers in Enantioselective Mukaiyama Aldol Reactions: Enzyme-Like Organocatalysis in Action
Luca Dell’Amico*, Franca Zanardi*
Abstract
Touched for the very first time! It is herein highlighted how acetaldehyde silyl enol ethers undergo enantioselective Mukaiyama aldol reaction with aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes. The chemistry relies on the use of the highly efficient and substrate‐selective imidodiphosphorimidate catalyst, which displays some of the features of enzymatic catalysis.
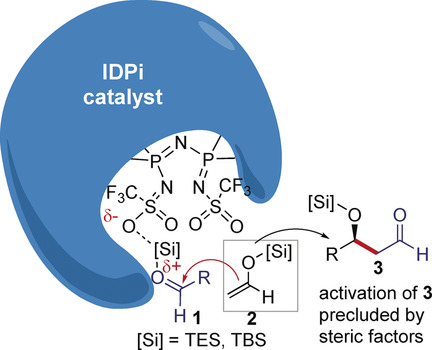
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3264-3266. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201812964
Microfluidic light-driven synthesis of tetracyclic molecular architectures
Javier Mateos, Nicholas Meneghini, Marcella Bonchio, Nadia Marino, Tommaso Carofiglio, Xavier Companyó* and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract
Herein we report an effective synthetic method for the direct assembly of highly functionalized tetracyclic pharmacophoric cores. Coumarins and chromones undergo diastereoselective [4 + 2] cycloaddition reactions with light-generated photoenol intermediates. The reactions occur by aid of a microfluidic photoreactor (MFP) in high yield (up to >98%) and virtually complete diastereocontrol (>20:1 dr). The method is easily scaled-up to a parallel setup, furnishing 948 mg of product over a 14 h reaction time. Finally, a series of manipulations of the tetracyclic scaffold obtained gave access to valuable precursors of biologically active molecules.
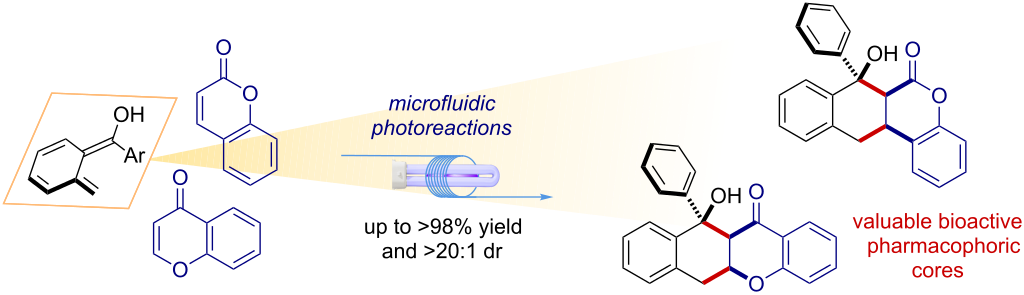
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018,14, 2418–2424. DOI :10.3762/bjoc.14.219
Transition Metal‐Free CO2 Fixation into New Carbon–Carbon Bonds
Alessio Cherubini‐Celli, Javier Mateos, Marcella Bonchio*, Luca Dell’Amico*, Xavier Companyó*
Abstract
CO2 is the ultimate renewable carbon source on Earth and the essential C1 building block for carbohydrate biosynthesis in photosynthetic organisms. Modern synthetic chemistry is facing the key challenge of developing fundamental transformations, such as C−C bond formation, in a sustainable and efficient manner from renewable sources. In this Minireview, the most significant methods recently reported for CO2 fixation under transition metal‐free conditions are summarized, organized into three different chapters according to the nature of the chemical transformation that forges the new C−C bond. The focus is on the mechanistic aspects of the different CO2 activation modes, with specific attention to those systems that operate under catalytic conditions.
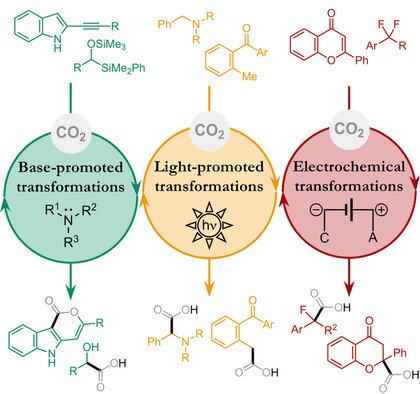
ChemSusChem 2018,11, 3056–3070. DOI : 10.1002/cssc.201801063
A microfluidic photoreactor enables 2-methylbenzophenone light-driven reactions with superior performance
Javier Mateos, Alessio Cherubini-Celli, Tommaso Carofiglio, Marcella Bonchio, Nadia Marino, Xavier Companyó* and Luca Dell’Amico*
Abstract
Light-driven reactions of 2-methylbenzophenones (2-MBPs) occur with improved yields (up to >98%) and reaction rates (up to 0.240 mmol h−1) by using a tailored microfluidic photoreactor (MFP). For the first time, coumarins were converted into 4-benzylated chromanones in high yields (50–93%) and diastereoselectivity (up to >20 : 1 dr), thus by-passing their photo-dimerisation end-reaction
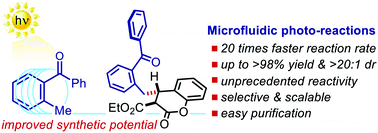
Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 6820-6823 . DOI: 10.1039/C8CC01373J
.
Books and book’s chapters
Modern Photocatalytic Strategies in Natural Product Synthesis
Sara Cuadros, Tommaso Bortolato, Alberto Vega-Peñaloza, and Luca Dell’Amico
Abstract
This book presents recent reports of total syntheses involving a photocatalytic reaction as a key step in the methodology.

Springer 2022. 10.1007/978-3-031-11783-1
Asymmetric Organocatalysis. New Startegies, Catalysts and Opportunities
Editors: Lukasz Albrecht, Anna Albrecht and Luca Dell’Amico
Abstract
The book provides a comprehensive overview of the most important advancements in the field of asymmetric organocatalysis that have occurred within the last decade. It presents valuable examples of newly developed synthetic methodologies based on various organocatalytic activation modes.
Special emphasis is given to strategies where organocatalysis is expanding its potential by pushing the boundaries and founding new synergistic interactions with other fields of synthetic chemistry, such as metal catalysis, photocatalysis, and biocatalysis. The application of different concepts (such as vinylogy, dearomatization, or cascade reactivity), resulting in the development of new functionalization strategies, is also discussed. Sample topics covered within the book include:
- New developments in enantioselective Brønsted acid catalysis with strong hydrogen-bond donors
- Asymmetric phase-transfer catalysis, from classical applications to new concepts
- Halogen-bonding organocatalysis
- Asymmetric electrochemical organocatalysis and synergistic organo-organocatalysis
- Immobilized organocatalysts for enantioselective continuous flow processes
- Mechanochemistry and high-pressure techniques in asymmetric organocatalysis
- Useful tools in elucidation of organocatalytic reaction mechanisms
With an overall focus on new reactions and catalysts, this two-volume work is an indispensable source for everyone working in the field of asymmetric organocatalysis.

Wiley, 2022, DOI: 10.1002/9783527832217
.
- Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11875-11879.
Forging Fluorine-Containing Quaternary Stereocenters by a Light Driven Organocatalytic Aldol Desymmetrization Process
- Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 3304-3308.
Light-Driven Enantioselective Organocatalytic β-Benzylation of Enals
- Chem. Rec. 2016, 16, 1787-1806.
Enantioselective Vinylogous Organocascade Reactions
- Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3313-3318.
Enantioselective Organocatalytic Diels–Alder Trapping of Photochemically Generated Hydroxy-o-Quinodimethanes
- Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 25, 7386-7390.
Organocatalytic, Asymmetric Eliminative [4+2] Cycloaddition of Allylidene Malononitriles with Enals: Rapid Entry to Cyclohexadiene‐Embedding Linear and Angular Polycycles
- J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11107-11114.
Exploring the Vinylogous Reactivity of Cyclohexenylidene Malononitriles: Switchable Regioselectivity in the Organocatalytic Asymmetric Addition to Enals Giving Highly Enantioenriched Carbabicyclic Structures
- Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 1561-1569.
Synthesis, Structure and Inhibitory Activity of a Stereoisomer of Oseltamivir Carboxylate
- Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 24, 5262-5265.
Asymmetric Organocatalytic Benzylation of α,β‐Unsaturated Aldehydes with Toluenes
- J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8063-8070.
Beyond Classical Reactivity Patterns: Shifting from 1,4- to 1,6-Additions in Regio- and Enantioselective Organocatalyzed Vinylogous Reactions of Olefinic Lactones with Enals and 2,4-Dienals
- Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 3278-3284.
Aqueous and Solvent‐Free Uncatalyzed Three‐Component Vinylogous Mukaiyama–Mannich Reactions of Pyrrole‐Based Silyl Dienolates
- Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 11, 1966-1972.
On‐Water Vinylogous Mukaiyama–Michael Addition of Heterocyclic 2‐Silyloxydienes to 1,2‐Diaza‐1,3‐dienes: One‐Pot Three‐Step Entry to Functionality‐Rich Pyrroles